Delivering working software in the hands of the customer is one of the core principles behind agile software development, and one that we follow at Webjet. This means teams break down their work into bite sized chunks and deliver working chunks iteratively.
But back when we started our agile journey, this usually meant working on the back end, followed by working on the front end. As you might have guessed it the “working software” was only delivered at or close to the very end. Not ideal.
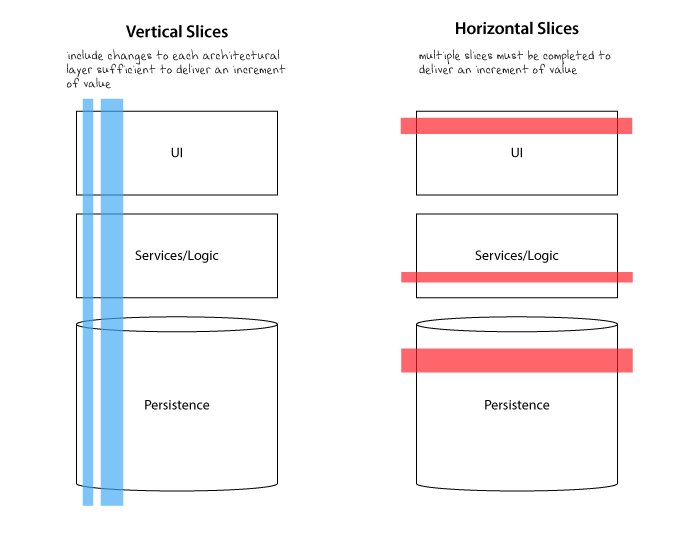
I didn’t know the word for it at the time, but we were doing Horizontal Slicing, i.e. breaking down work based on its functional area, without taking a holistic end to end approach. We were iteratively delivering a car by delivering only the wheels first.
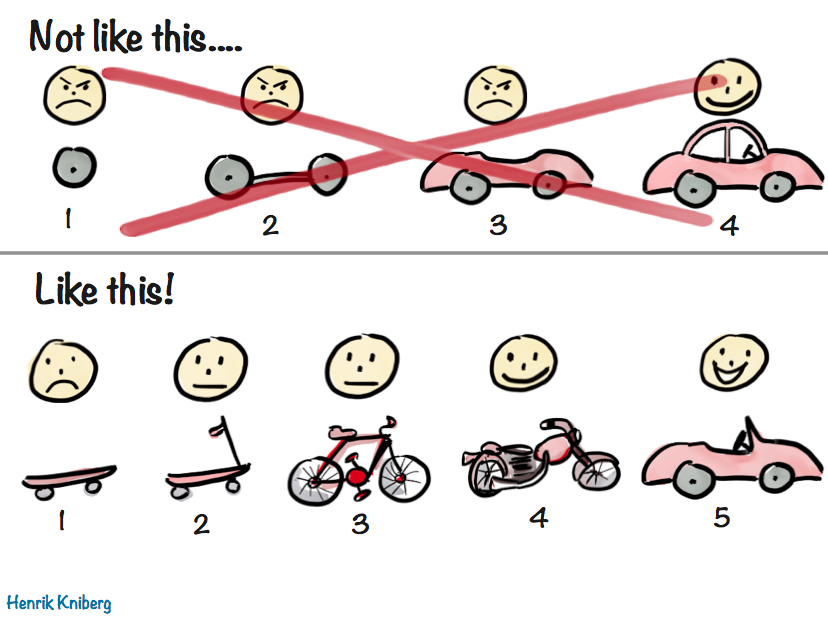
Going back to the core principles, we looked at how we can deliver a true MVP, something that provides value to the customer and to the company, something that we are happy to have in production. We came across the concept of vertical slicing, which helped us articulate the MVP approach.
Using the example of creating a new flight search experience for mobile browsers, I will share our thinking and how we approached vertical slicing, which will help crystalize the concept
Our flight search experience for mobile needed an update. The incumbent design was a copy of the legacy app experience, built using JQuery mobile integrated into our monolith. This made making changes more complicated and take longer to deliver. It was not aligned with our strategy of splitting it into independently deployable microservices.
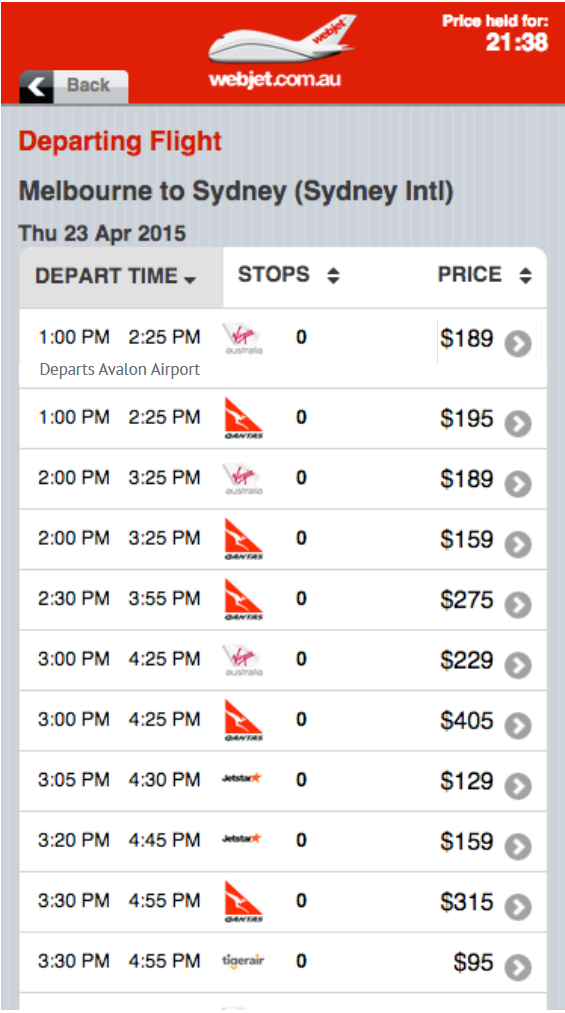
We decided to create a new React based service to render the responsive front end coupled with a new search API. This would make iterative changes less complex and faster to market. But there were a lot of features to deliver, multiple result views, and the integration with the legacy platform.
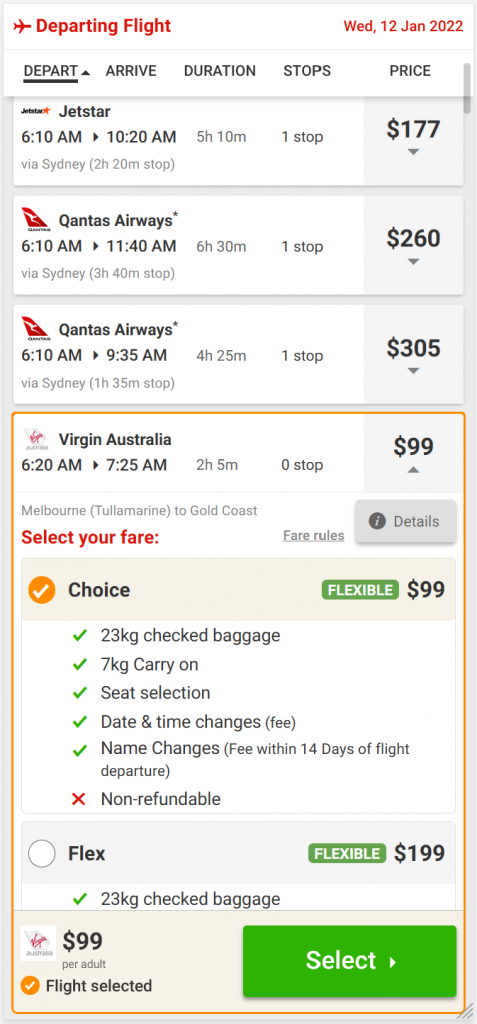
To help define the workflow the team documented the high level workflow
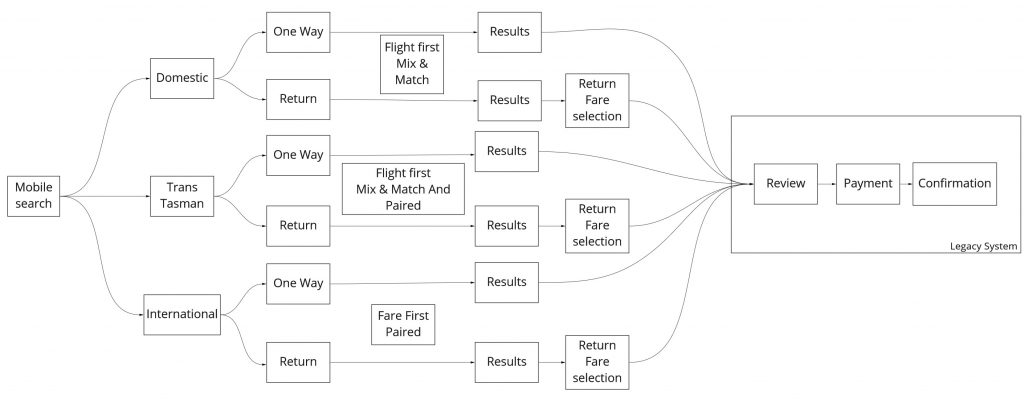
To help guide our decision in defining the MVP we looked at the following
- Data on the booking mix i.e. domestic vs Trans-Tasman vs international, one-way vs return, passenger mix etc
- Key path dependencies
- An MVP that delivers value to the customer
The following were the results of the analysis
- A large majority of the bookings were domestic, so the real value from a customer’s POV lay there
- As domestic volume was higher any issues in the new path could be amplified
- A wide range of passenger mixes existed, e.g. 1 adult, 2 adult and 1 child, 2 adults etc
- Integrating into the legacy shopping cart was a key dependency. Until now the search and booking happened in the same platform.
- The incumbent mobile design was quite dated and had limited functionality. Customers could only sort on 4 attributes and there was no filtering
Based on this we determined the first slice as a
- Single one-way adult search: limits the scope of the customer cohort
- For a medium capacity route: reduces the risk of unexpected failures and provides value to the customer
- With just the sort functionality currently supported: limits the feature set that needs to be built
- That can be searched and booked end to end: reduces key path dependency
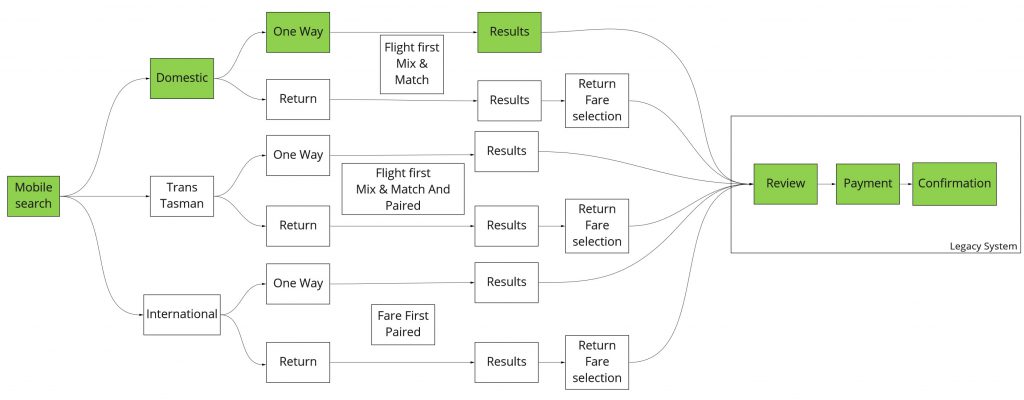
The team went on to develop this MVP and release it to the customers in a fraction of the time of the full design build. After based on feedback from data gathered, we iteratively added more features starting with supporting return search and result filtering. The team could quickly support more routes and passenger mixes using feature flags as their confidence grew in the new services.
Not only were we able to deliver value iteratively, but since we only focused on a narrow path it gave other advantages
- Validation of the new design in the hands of the customers
- The team did not need to develop a Trans-Tasman or an international design till much later
- Increased confidence in monitoring and alerting of the service as the load slowly increase
Looking back at our approach the key element that made this a success was a strong engagement with the business stake holders. Having their input and buy in to delivering a fraction of the promised functionality in the customer’s hands was crucial. We used real metrics to measure customer satisfaction with our new design. It also helped us tweak features that were causing issues and iterate on the features that were well received.
Without it we would be relegated to releasing in our UAT environment which would not give true confidence in the design, and customer would have waited months to get any value.
If you are interested in joining our team, we are hiring!
Our current job postings can be found here: https://lnkd.in/gycBPXPx


